Papers on graph convolution
Why are graph neural net worth of your interest ?
Because of the applications, it ranges from 3D mesh object to recommandation with rich data annotation. The only problem it has, is that application of neural networks is non trivial. There is no obvious, built in graph operator. Different applications usually require different ways of treating the information. This is why I will present some papers that use various methods.
Insighful articles on graph convolution and graph pooling
Variational Autoencoders for Deforming 3D Mesh Models
This paper presents a simple way to use regular 3D mesh.
Main elements :
- Dataset of moving characters : same topology for all elements
- RIMD representation that is rotation and scale invariant
- Fully connected auto encoder as usage is straight forward
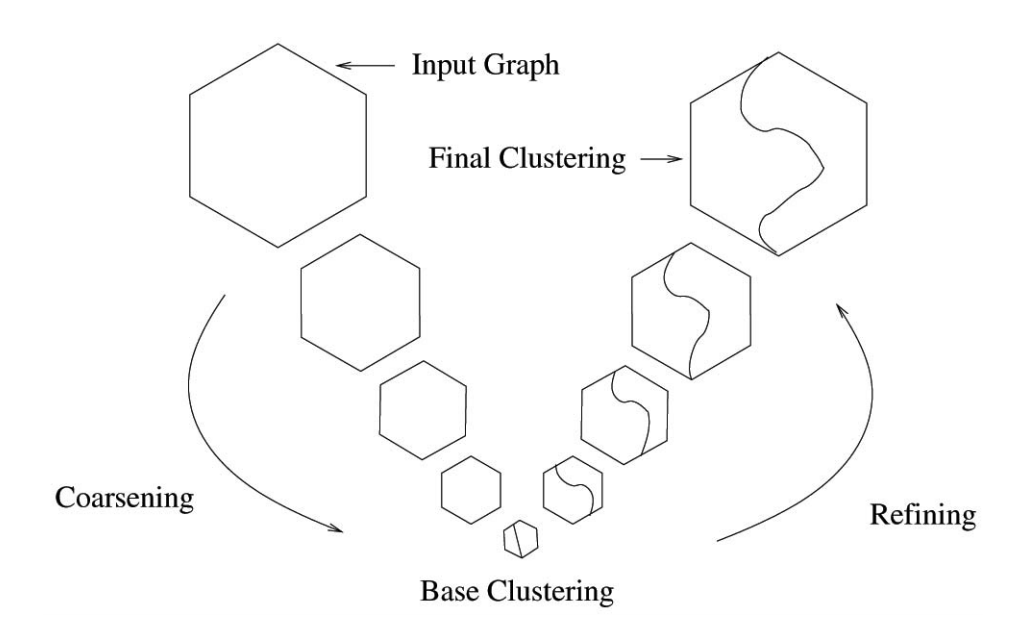
Weighted Graph Cuts without Eigenvectors: A Multilevel Approach
This paper presents the fundamental Graclus algorithm used to build a pooling operation for graphs.
This paper presents a way to do clustering on large scale graph through a hierarchical strategy. The Graclus pooling method allows to reduce the original graph to a reasonable size. From the labels extracted from the higher order graph, a refinement strategy allows to propagates the labels to all lower order graphs until the initial one is reached.
A figure from the paper illustrates this idea for a clustering algorithm with 2 clusters.

Coarsening phase :
- Start with all nodes unmarked
- Select all nodes in random order
- Merge the selected node with the node having the highest weight
- If there is no other node, the node is merged with itself
Possible wieghts for the algorithms are edges weights or \(weight_{edge}(x, y) / connectivity(x) + weight_{edge}(x, y) / connectivity(y)\)
Refinement step : Once the labels are extracted from the high order graph, we need to propagate them to lower order graph to have a label on all final nodes. This paper suggests to change the label of nodes that are neighbours to another super node. And change assignments of this node only according to a weighted kernel k-mean procedure. It is also precised that incremental k-mean also performs much better.
- Given i-th order graph \(G_i\) with labels for all nodes \(n_{gi}\), assign nodes label to \(G_{i-1}\).
- Define boundary nodes as nodes having edges to nodes with different labels.
- For the boundary points, test if switching labels improves the considered clustering metric.
Graph Convolutional Neural Networks for Web-Scale Recommender Systems
This paper presents a collections of technics that were used to efficently extract value from graph data at Pinterest.
Main steps :
- Localized convolution : Use a sub part of the graph for conv
- Convolution with random walk : sampling of the neighbourhood of nodes using a random walk importance sampled with edge weights
- Importance pooling : Use random walk to generate weights that can be used to do sample pooling
- Curriculum training and efficient map reduce schema
The neighbourhood feature is defined as the weigthed mean of the neighbourhood nodes features. The neighbourhood is defined thanks to the weights extracted through random walk.
The pooling is done in an inverse manner, we first select the nodes we want to have after the k convolutions. For batch b, we select n_batch nodes N and wish to stack K convolutions. We thus proceed to build S(k) recursively with S(K) = {N} and S(k-1) = S(k) + neighbourhood(k)
For each phase k, a neighbourhood convolution is performed on all the neighbourhood of each node of S(k). After it, for each node, the embedding of the next layer is computed with the current embedding of the node and the one of the neighboorhood.
The article provides a clean summary of the algorithm.

Additional trick used to scale :
-
Handling large scale data : Split the nodes in the graph in a hash ring manner, add all the neigbourhood of the all nodes in the subgraph to be able to run batches.
-
Deep embedding computed via map reduce : One job for neigbourhood feature and one job for next layer feature computation.